Oscillation in counter-phase and multiple potential division sites in long extended filaments
In filamentous cells, MinD (and associated MinC) dynamically accumulates on multiple regularly-spaced membrane segments along the length of the filaments, and these maxima oscillate in counter-phase over time. As in WT cells, this dynamic behavior of MinC/D requires the presence of MinE. The figure below shows this behavior of Gfp-MinD in time-lapse fluorescence micrographs.
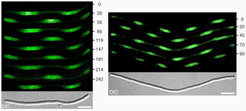
Time is indicated in seconds. The bottom panels show the filaments viewed with DIC optics. The bars represent 5 µm. Shown are cells of strain DR102(lDR122)/pDB346 [DminCDE, ftsZo (Plac::gfp-minD, minE)/PlR::ftsZ, cI857]. Cells were grown at 30oC (resulting in repression of ftsZ expression) in minimal medium supplemented with 37 mM IPTG. For additional details, see [1,2] The corresponding dynamics of MinE in such filaments can be viewed here.
In the models, in a cell surpassing a critical size due to an inhibition of cell division, a transition occurs from one to two zones in which MinE sweeps back and forth. The positioning of the FtsZ pattern(s) follows the corresponding change in the distribution of MinD. The following simulation shows counter-phase oscillation in a medium-size filament with two potential divisions sites.
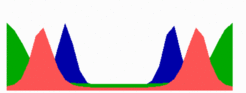
The close correspondence between experimental observation and model calculation becomes even more obvious by plotting only MinD with a pixel density proportional to the local concentration:
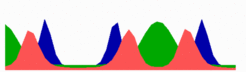
The number of MinE waves that are present simultaneously equals the number of potential division sites, and this number increases with field size. FtsZ accumulates in the regions with the lowest time-averaged concentrations of MinD:
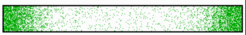
The following simulations shows the MinD as well as MinE patterns with a pixel density proportional to the local concentration in a larger field :

References
- Raskin, D. M., and de Boer, P. A. J. (1999). MinDE dependent pole-to-pole oscillation of division inhibitor MinC in Escherichia coli., J Bacteriol 181, 6419-6424.
- Raskin, D. M., and de Boer, P. A. J. (1999b). Rapid pole-to-pole oscillation of a protein required for directing division to the middle of Escherichia coli., PNAS 96, 4971-4976.




